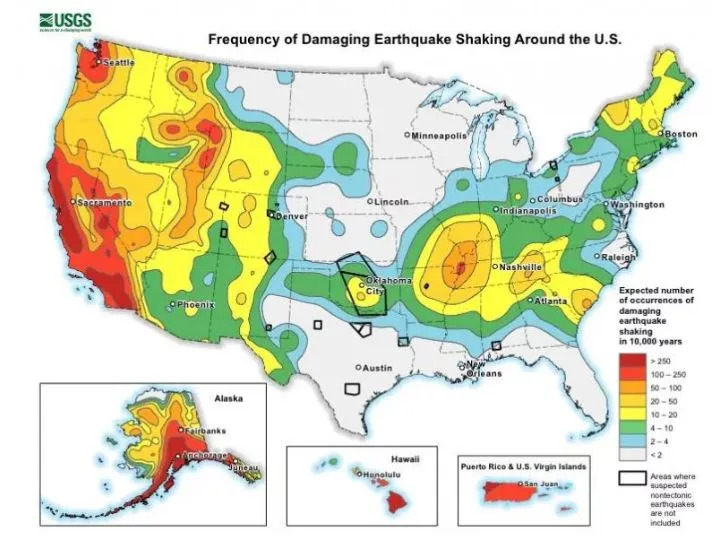
Apparently, everything that was known about seismic movements in the north of the American continent has changed. More states are on the alert list thanks to new discoveries made by scientists, combining technology and mapping.
In addition, if the damage suffered is to be as little as possible, it is essential that society is educated and that infrastructures are improved.
New earthquake spots
As we already know, the United States extends over numerous seismic faults, which has affected, affects and will affect several states.
Although enlarging the list of states is not good news, it is thanks to science that this new information is available and action can be taken.
By combining data analysis with modern mapping techniques, it has been possible to detect a widening in the size of many existing faults, resulting in a wider range of potential surface damage.
Why is this useful? Because it facilitates the work of scientists and professionals, who will be able to predict these earthquakes with greater precision.
What are the new affected states?
Logically, any area that is located on an earthquake fault must have higher priority than others, since it needs foresight, infrastructure preparation and mitigate the possible consequences.
First, the west coast. Until now, all eyes were on the San Andres Fault in the state of California. The data prior to this discovery mapped a particular area of the fault, which has proved to be erroneous. Now, Los Angeles and San Francisco must join the spotlight.
The Cascadia subduction area has always been considered a risk zone, but is now extended to any state or border area. Thus, the state of Oregon and the south of the state of Washington are added.
Furthermore, the states of Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee and Kentucky also join to the high-risk list. The latest study reveals an increase in seismic movement in this area, although it has not yet been possible to map and define the affected territory with precision. However, the eyes are on the seismic zone of Nuevo Madrid, which affects regions of central North America.
How do I know if my status is prepared for natural catastrophes?
There are several aspects that any region affected by seismic movements or dangerous natural phenomena must have on its to-do list.
It is necessary to create strict rules when building. Not worth any material or design. They must have plans developed by professionals, so that all the constructions can withstand the jolts of the tremors, without breaking.
In addition, it is essential that these areas have well-structured and defined evacuation plans, which are known and practiced through regular drills. All homes, public and private institutions and any place where citizens can be safeguarded in the event of an emergency should have supplies.
What solutions can we rely on?
Obviously, there is no solution when it comes to natural phenomena. It’s something that gets out of our hands. However, we can and must put all our attention on technology and advances in science.
The only place where human beings can exercise some kind of control over these types of events is in mitigation and forecasting. Thanks to technological advances, it has been possible to develop techniques for identifying patterns of behavior in seismic movements through data analysis.
Earthquake simulators have been developed, enabling professionals to predict, understand and learn how to act before, during and after earthquakes.
It is the job of institutions, professionals, society and each citizen to be well informed, apply the rules and measures imposed in these cases and fulfill the function they have to perform, so that everyone’s safety is guaranteed.
If you want to know more about the behavior of this type of phenomena, read the following article.